Choosing between a franchise and an independent business is a pivotal decision for aspiring entrepreneurs. This article delves into the critical pros and cons of each model, examining factors like startup costs, brand recognition, operational support, marketing assistance, profit margins, and risk tolerance to help you determine which path best aligns with your business goals, financial resources, and risk appetite. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of franchise ownership versus establishing an independent venture is crucial for making an informed choice that maximizes your chances of success.
Understanding the Key Differences
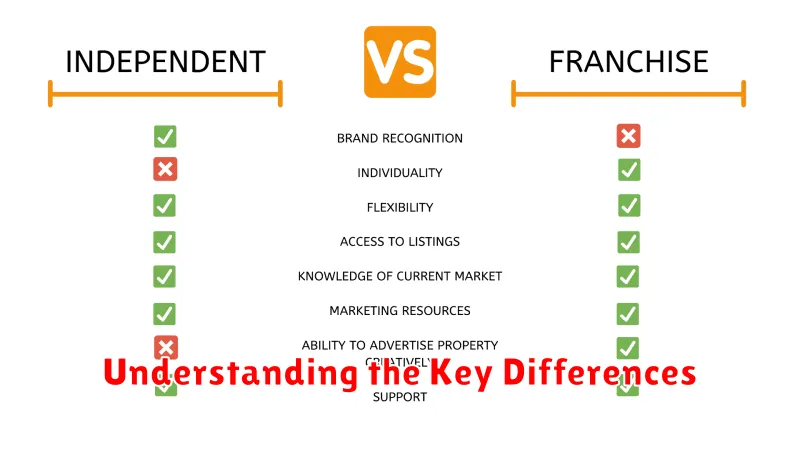
The primary distinction lies in ownership and control. A franchise involves purchasing the right to operate a business under an established brand, adhering to its systems and guidelines. This provides brand recognition and operational support but limits autonomy. An independent business, conversely, offers complete ownership and control, allowing for greater flexibility and creativity but requiring independent brand building and operational management.
Financial investment also differs significantly. Franchises often demand a substantial initial fee and ongoing royalties. Independent businesses typically require less upfront capital but securing funding may be more challenging. Profit sharing is another key difference; franchisees share profits with the franchisor, while independent business owners retain all profits (after expenses).
Risk and reward are intrinsically linked to these differences. Franchises offer a proven business model, reducing the risk of failure, but limit profit potential due to shared earnings and operational constraints. Independent businesses carry higher risk, dependent on the entrepreneur’s skills and market conditions, but offer the potential for greater financial reward.
Finally, support and training vary greatly. Franchises provide extensive training and support, including marketing and operational assistance. Independent businesses must independently acquire these resources, adding to the initial challenges.
Pros and Cons of Buying a Franchise
Buying a franchise offers several advantages. Established brand recognition and a proven business model significantly reduce the risk of failure. Franchises often provide comprehensive training and ongoing support, easing the burden on new business owners. Access to established supply chains and marketing resources can also lead to cost savings and increased sales. Financing may also be easier to secure due to the lower perceived risk.
However, there are also disadvantages. Franchise fees and royalties can represent a substantial ongoing cost, reducing profitability compared to an independent business. Franchisees typically have limited control over operations and marketing decisions, adhering to the franchisor’s guidelines. The success of the franchise is partly dependent on the franchisor’s performance and reputation, leaving franchisees vulnerable to external factors outside their control. Competition within the franchise system itself can also be a challenge.
Advantages of Starting an Independent Business
Starting an independent business offers several key advantages. Complete creative control is a major draw, allowing entrepreneurs to build a brand and offer products or services exactly as they envision. This extends to pricing strategies and marketing approaches, providing flexibility unavailable within a franchise structure.
Higher profit potential is another significant benefit. While franchise fees and royalties reduce earnings in a franchise model, independent businesses retain all profits after expenses. This can lead to faster growth and a greater return on investment.
Finally, independent business ownership offers a greater sense of personal fulfillment and independence. The ability to set one’s own hours, build a unique business culture, and pursue personal passions is often a powerful motivator for entrepreneurs.
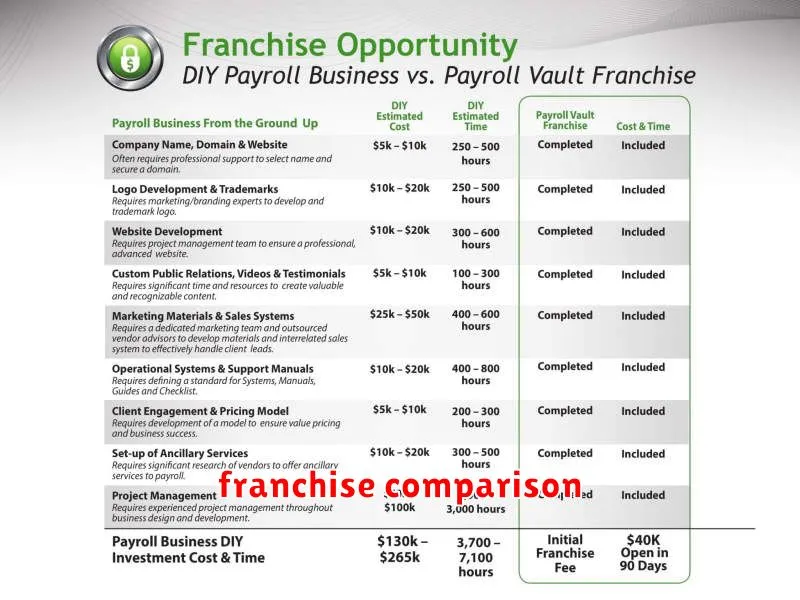
Cost Comparison: Franchise vs Self-Owned
Starting a franchise typically involves higher initial costs. These include a significant franchise fee, ongoing royalty payments, and potentially advertising fees. However, the established brand recognition and operational systems can often lead to faster revenue generation.
A self-owned business generally requires lower initial investment, but securing funding and building brand awareness can be challenging and time-consuming. Startup costs will vary significantly depending on the industry and business model, encompassing expenses like equipment, inventory, marketing, and potentially rent or leasehold improvements.
Ongoing expenses also differ substantially. Franchises have consistent royalty payments, while independent businesses bear the full responsibility for all operating costs. Therefore, a thorough financial analysis comparing projected revenue and expenses is crucial for both models to determine overall profitability and return on investment.
Branding and Marketing Support in Franchising
One significant advantage of franchising over starting an independent business lies in the area of branding and marketing. Franchise systems typically provide extensive support in this crucial area.
Established franchises offer a pre-built brand with existing customer recognition and loyalty. This eliminates the time, cost, and risk associated with building brand awareness from scratch.
Franchisors often provide comprehensive marketing materials, including advertising templates, social media strategies, and point-of-sale displays, leveraging economies of scale for greater impact. They may also offer training and guidance on effective marketing techniques.
Furthermore, many franchisors engage in co-op marketing, pooling resources from multiple franchisees for regional or national advertising campaigns, maximizing reach and minimizing individual franchisee costs. This collaborative effort enhances brand visibility significantly.
Access to a proven brand and established marketing infrastructure can provide a competitive edge and contribute significantly to a franchisee’s success. This support is a key differentiator between franchising and independent business ventures.
Flexibility and Control in Independent Businesses
One of the most significant advantages of starting an independent business is the unparalleled flexibility and control it offers. Unlike franchisees who must adhere to strict brand guidelines and operational procedures, independent business owners enjoy complete autonomy in shaping their business model.
This freedom extends to various aspects, including product offerings, pricing strategies, marketing approaches, and operational procedures. Independent business owners can adapt swiftly to changing market demands and consumer preferences, fostering innovation and responsiveness.
Furthermore, the control over all aspects of the business allows for greater alignment with personal values and goals. Owners can build a company culture reflective of their vision and create a work environment that prioritizes employee well-being and satisfaction. This autonomy, however, comes with increased responsibility and risk, as the success or failure of the business rests entirely on the owner’s shoulders.
This high degree of control can be both a blessing and a curse; while it allows for personalized growth and creative freedom, it also necessitates a broader skill set and a greater capacity to bear risk. The ultimate trade-off between the advantages and the responsibilities of independent ownership needs to be carefully considered.
Long-Term Profitability: Which One Wins?
Long-term profitability depends heavily on various factors, making a definitive “winner” between franchises and independent businesses impossible to declare. However, some key differences impact the likelihood of success.
Franchises often benefit from established brand recognition, proven business models, and ongoing support from the franchisor. This can lead to quicker initial profitability and reduced risk, particularly for first-time entrepreneurs. However, franchise fees and royalties can significantly impact profit margins, potentially limiting long-term growth compared to a successful independent venture.
Independent businesses offer greater flexibility and control. Owners can adapt their strategies and offerings to better suit market demands and build unique brand loyalty. While this potential for high rewards exists, the absence of established systems and brand recognition increases the risk and requires a stronger entrepreneurial skill set and potentially higher initial investment to achieve sustained profitability. Profitability hinges on the owner’s ability to effectively manage all aspects of the business and adapt to market changes.
Ultimately, long-term profitability is determined by effective management, market conditions, and the owner’s entrepreneurial acumen. Neither a franchise nor an independent business inherently guarantees success; careful planning and execution are crucial for achieving sustained growth and financial success in both models.
How to Decide Based on Your Goals and Resources
Choosing between a franchise and an independent business hinges on your goals and available resources. Consider your risk tolerance: franchises offer established systems but require significant upfront investment and ongoing royalties. Independent businesses offer greater flexibility and control but demand more entrepreneurial effort and carry higher risk.
Financial resources are critical. Franchises necessitate substantial initial fees and ongoing operational costs. Independent businesses require funding for startup costs, marketing, and ongoing expenses, potentially requiring securing loans or investor funding. Assess your financial capacity to sustain operations through potential lean periods.
Your personal goals should also inform your decision. Do you prefer a structured, proven business model (franchise) or the freedom to create and build something unique (independent)? Consider your time commitment; franchises might offer more structured support but still require significant hours. Independent businesses demand even more personal time and dedication.
Finally, evaluate your skills and experience. Franchises provide training and support, benefiting those with limited entrepreneurial experience. Independent businesses require a diverse skill set and the ability to manage multiple aspects of the business independently. Carefully assess your strengths and weaknesses.